Pipe Network 2-Axes Template with SFC, ST, FFLD, and FBD
PLC Programs
The 2-axes Pipe Network template has an SFC![]() "Sequential function chart"
It can be used to program processes that can be split into steps.
The main components of SFC are:
- Steps with associated actions
- Transitions with associated logic conditions
- Directed links between steps and transitions program (called Main) that initializes and starts the motion.
"Sequential function chart"
It can be used to program processes that can be split into steps.
The main components of SFC are:
- Steps with associated actions
- Transitions with associated logic conditions
- Directed links between steps and transitions program (called Main) that initializes and starts the motion.
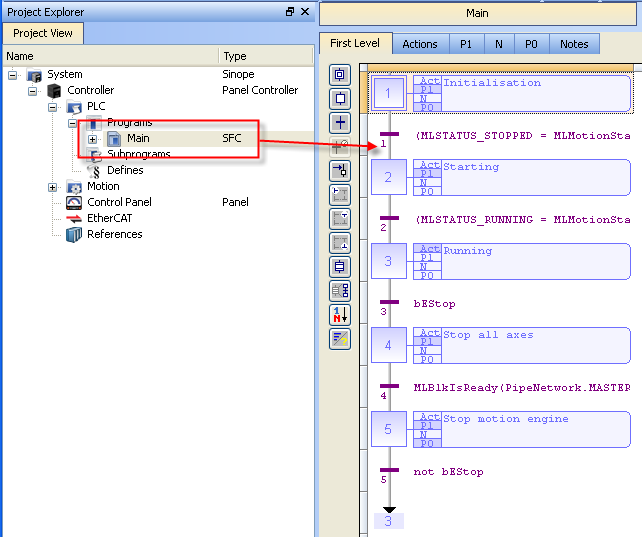
Figure 7-34: PN Template - Main
The Pipe Network Template contains an SFC child program called Machine Logic for running motion.
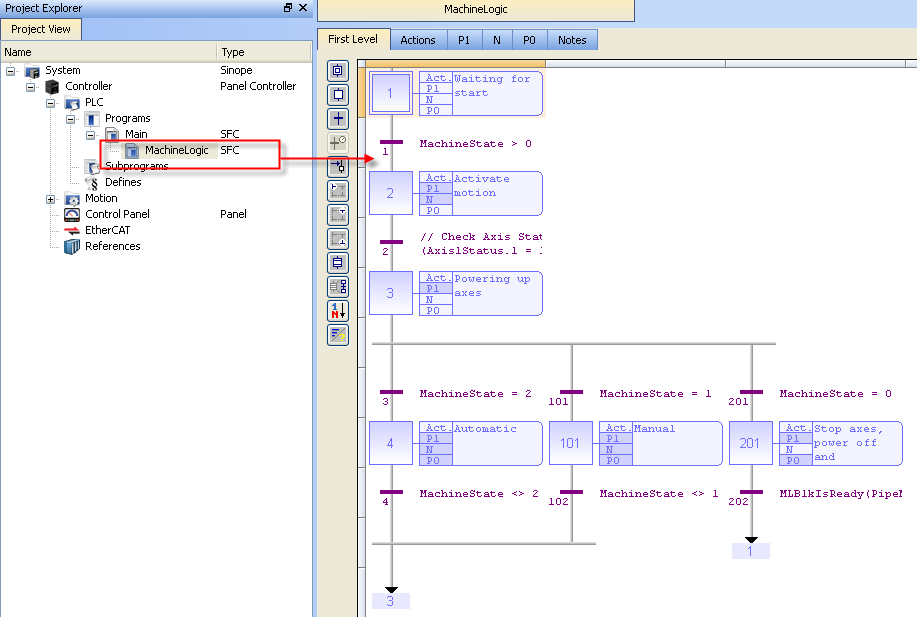
Figure 7-35: PN Template - MachineLogic
ST![]() "Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal programs can be found in the P1 and P0 actions for many steps
"Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal programs can be found in the P1 and P0 actions for many steps
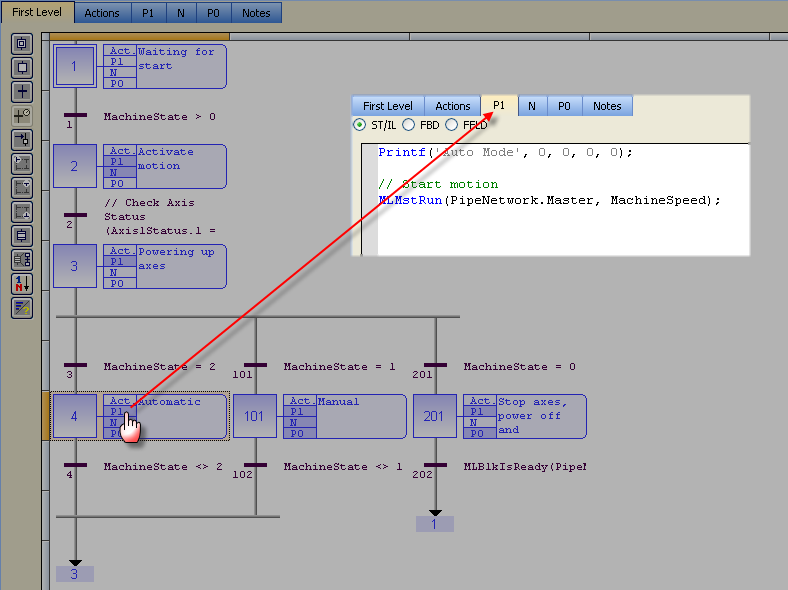
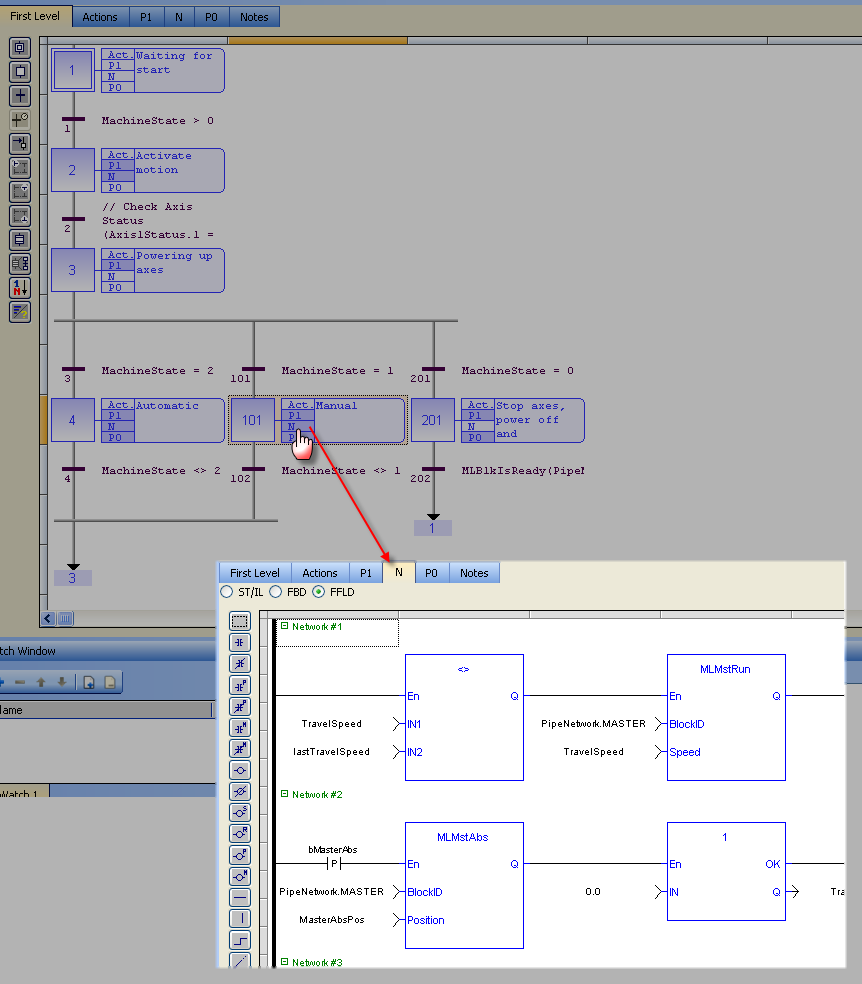
FFLD programs can be found in the N action for steps 4 and 101
Motion
The template has a motion profile defined with the graphical Pipe Network editor.
For more details, see sPipe Blocks Description
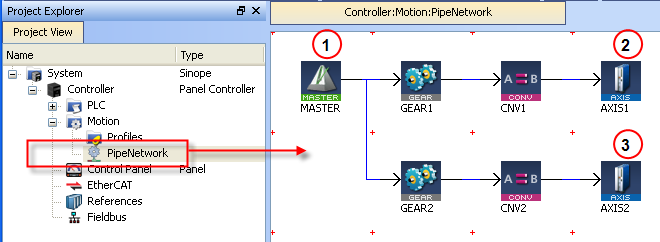
Figure 7-36: PN Template - Motion
The motion profile contains four different pipe blocks:
- The Master (see call out
 ) is the generator that allows a synchronization between the two pipes (
) is the generator that allows a synchronization between the two pipes ( and
and  ).
). - The Gear modifies (with ratio and offset) the flow of values issued from the Master.
- The Convertor controls the position of the axis.
- The Axis gives access to the physical remote drive
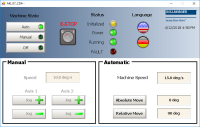
Control Panel
For more details, see Design the Control Panel with the Internal Control Panel Editor
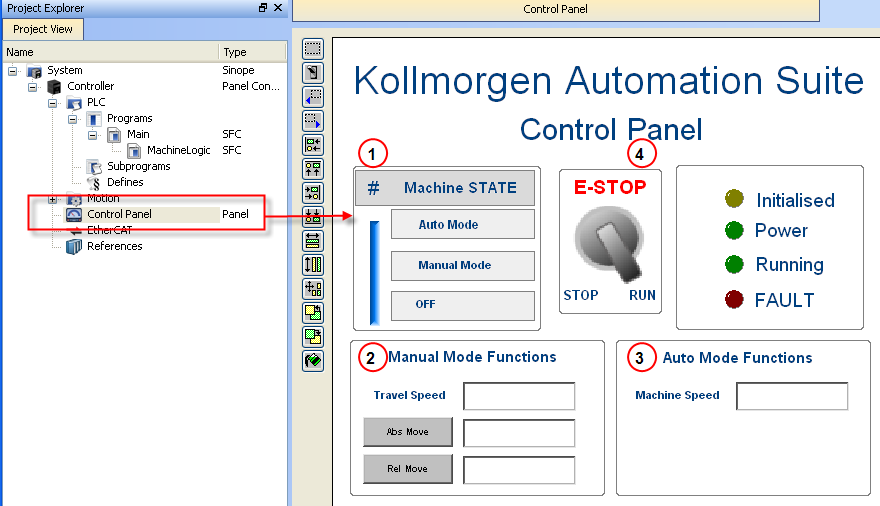
Figure 7-37: PN Template - Control Panel
|
Call out# |
Description |
|
|
Allows to choose how to run the axes between automatic and manual modes |
|
|
In manual mode, you can set the speed. You can also set an absolute and relative move. When you click those commands, the two axes move to the specified position and the speed is reset to 0 |
|
|
In automatic mode, you can set the speed |
|
|
When you click the emergency button, the machine state becomes OFF (see call out |
Table 7-35: PN Template - Control Panel
Based on the template, the project can be run:
- using the KAS Simulator
- with actual drives and motors (in this case, you first have to set up the axes in the EtherCAT
 ***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs part. For more details, see "Configuring EtherCAT")
***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs part. For more details, see "Configuring EtherCAT")
HMI
Also included in the project template is an HMI![]() "Human-machine interfaces "
Also known as computer-human interfaces (CHI), and formerly known as man-machine interfaces, they are usually employed to communicate with PLCs and other computers, such as entering and monitoring temperatures or pressures for further automated control or emergency response screen for the AKI terminals created in the KVB (Kollmorgen Visualization Builder) environment.
"Human-machine interfaces "
Also known as computer-human interfaces (CHI), and formerly known as man-machine interfaces, they are usually employed to communicate with PLCs and other computers, such as entering and monitoring temperatures or pressures for further automated control or emergency response screen for the AKI terminals created in the KVB (Kollmorgen Visualization Builder) environment.
The KVB software is a separate installation from the KAS IDE![]() "Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger. KVB can be opened from within KAS IDE by double-clicking on the KVBProject item in the project tree.
"Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger. KVB can be opened from within KAS IDE by double-clicking on the KVBProject item in the project tree.
The project can be run in the KVB programming environment after the KAS IDE program has started running. Click on the Run button in the Project ribbon to start the program.
A screen, localized in English and German, is included which duplicate the controls on the IDE Internal Control panel screen.